Feature of Operations
SME Unit's Clients
SMEs and micro/small businesses account for 99% of all businesses in Japan, and are both the source of Japanese economic vitality as well as the primary force underpinning regional economies.
The size and conditions of each SME and micro/small business differ, such as companies that sustain the regional economy with many employees, long-established companies with a history over 100 years and family-owned private shops.
The SME Unit provides a wide range of support to meet the individual needs of each SME and micro/small business through its financial tools, Loan Programs, Credit Insurance Programs and Securitization Support Programs.
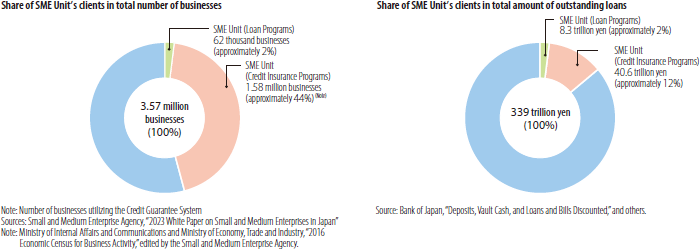
The SME Unit facilitates funds to 1.64 million SMEs and micro/small businesses (approximately 46%) and accounts for 14% of outstanding loans to SMEs and micro/small businesses.

Note: Results are current as of March 31, 2023.
The SME Unit also helps to maintain employment, with the number of employees at the 62 thousand businesses having approximately 3.84 million persons (as of March 31, 2023) by direct loans.
Loan Programs
Supplementing private financial institutions both in quality and quantity with a stable supply of long-term funds
- Dedicated to long-term funding
If SMEs are to grow and prosper, they must continually invest capital appropriately and consolidate their financial strength. To do this, they need to be able to raise long-term funds in a stable manner.
However, SMEs are at a disadvantage to larger enterprises in gaining access to funds from capital markets.
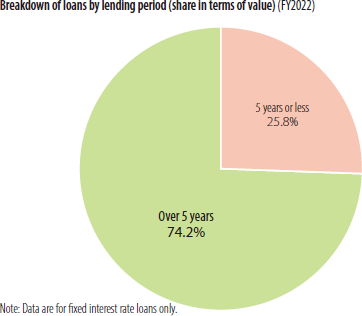
The SME Unit specializes in long-term funds. More than 50% of the SME Unit's loans have lending periods of over 5 years, with fixed interest rates that make it easier to map out repayment schedules.
By complementing private financial institutions, the SME Unit meets the long-term funding needs of SMEs, which are a vital component of the Japanese economy.
- Stable supply of business funds
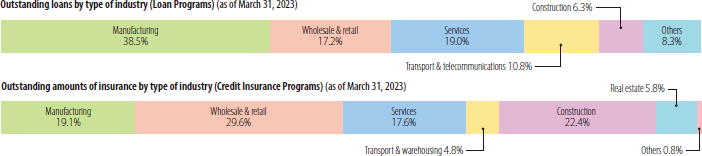
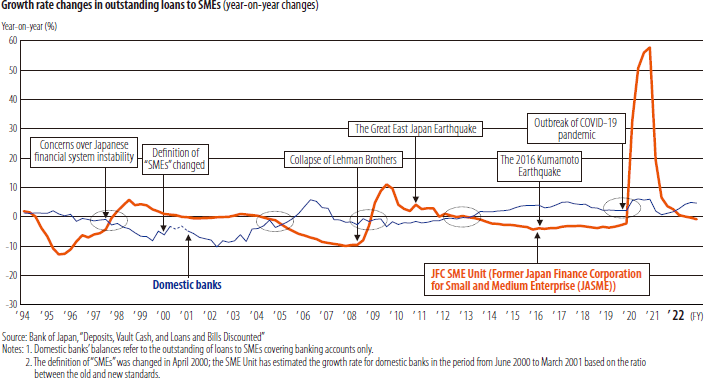
Growth in loans to SMEs was high during the economic downtown precipitated by the collapse of Lehman Brothers and conversely has been declining during the period of economic recovery.
Over the years, the SME Unit has provided SMEs with stable, long-term business funds by supplementing private financial institutions.
Promoting special-purpose loans based on government policies to meet the needs of the times
- Safety net
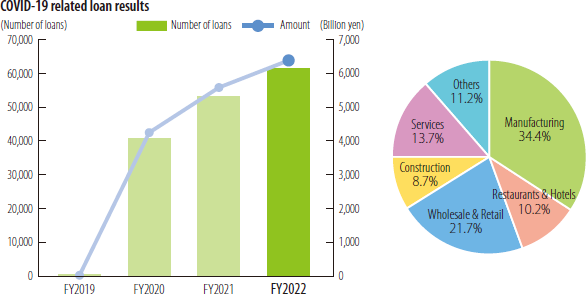
Although the initial emergency demand for funds when the COVID-19 pandemic first spread has subsided, due to the prolongation of the pandemic, we continued to support cash flows and business reconstruction by providing loans for SMEs through Safety Net Loans and COVID-19 Special Loan Program, and other programs, as in the previous fiscal year.
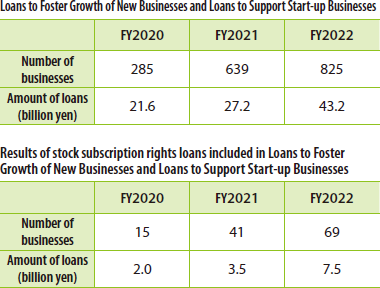
- Supporting new businesses and start-ups
The SME Unit provides active support to SMEs trying to develop new businesses with high growth potential through Loans to Foster Growth of New Businesses and to start-ups that are expected to lead Japan's economic growth and solve social problems through Loans to Support Start-up Businesses. Since the program began, the cumulative total (Note) (as of March 31, 2023) has reached 15,963 businesses, amounting to 769.3 billion yen. In addition, the SME Unit also offers Stock Subscription Rights Loans, an unsecured loan program through the acquisition of new share options issued by companies.
Note: Loans to Foster Growth of New Businesses was launched in February 2000, and the Loans to Support Start-up Businesses was launched in February 2023. Loan performance includes Hybrid Subordinated Loan Program.
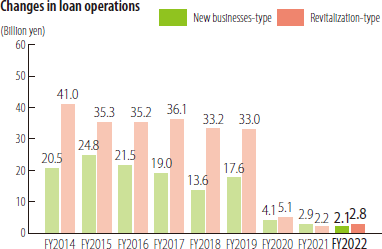
- Capital subordinated loans
The SME Unit supports reinforcing the financial standing of SMEs engaged in new businesses and business reconstructions, by applying the Hybrid Subordinated Loan Program (former Provision Scheme for Challenge Support and Capital Enhancement) in cooperation with private financial institutions. Liabilities under this provision scheme may be treated as shareholders' equity under the borrower classifications determined by financial institutions.
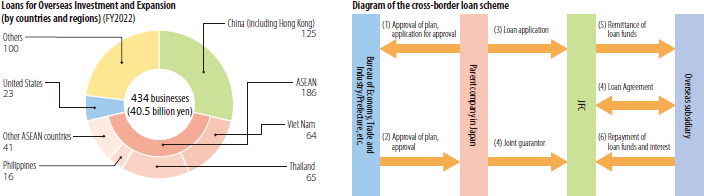
- Support for overseas investment
The SME Unit provides active support for the overseas expansion of SMEs, such as providing Loans for Overseas Investment and Expansion, supporting the fundraising by SMEs' overseas subsidiaries and branches through the Standby Letter of Credit Program and cross-border loans, offering management consulting services and holding business network meetings abroad.
In FY2022, Loans for Overseas Investment and Expansion were utilized by 434 businesses, for a total of 40.5 billion yen.
The Standby Letter of Credit Program supports SMEs and micro/small businesses' overseas subsidiaries' and branches' smooth procurement of long-term local currency denominated funds from JFC's partnering overseas financial institutions by using JFC's standby letter of credit as a guarantee. As of March 31, 2023, the number of affiliated financial institutions, mainly in Asia, was 15 institutions.
JFC also established a scheme to partner regional financial institutions throughout Japan, and through the end of March 2023, JFC established collaborative relationships with 61 regional financial institutions.
As for FY2022, letters of credit were issued to the financial institutions in 9 countries and regions, being utilized by 82 businesses.
The cross-border loans are a program under which JFC provides direct loans to overseas subsidiaries. The countries and regions where this program can be used are Thailand, Viet Nam, Hong Kong, Singapore, and the Philippines, and loans were provided to 94 borrowers, 7.6 billion yen in FY2022.
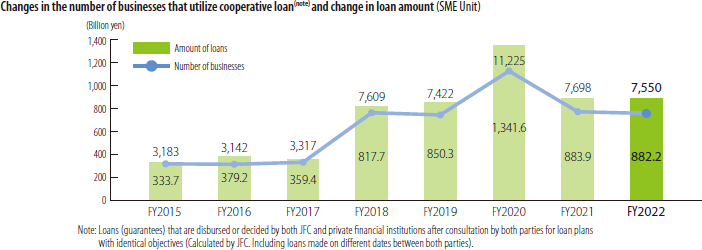
- Cooperative loans and securitization support in collaboration with private financial institutions
The SME Unit makes use of various functions including loans, securitization support, and credit guarantees as well as the screening capabilities that it has accumulated over many years and information in a database of approximately 62,000 customers nationwide to collaborate with private financial institutions and provide support to SMEs in the areas of business start-up and new business, overseas expansion, rapid business revitalization, business succession, securitization, management consultation, and human resource development. Specific activities include close exchanges of information with private financial institutions, support for cooperative loans, and joint sponsorship of business matching events and seminars on overseas business development and business succession.
In particular, since FY2018 the SME Unit has actively undertaken collaboration with private financial institutions by promoting collaborative measures with private financial institutions to enter a new stage. In response to the COVID-19 pandemic, we also provide financial support to affected SMEs based on existing cooperative relationships.
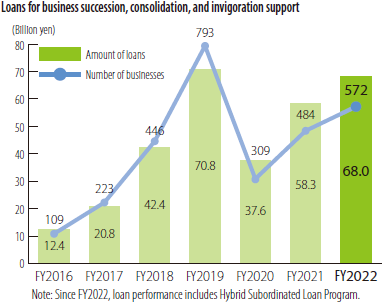
- Loans for business succession, consolidation, and invigoration support
The SME Unit provides support through special loans for business succession, consolidation, and invigoration support so that SME without a successor can carry out M&A or acquire their own shares in order to secure stable management rights so that they can carry out succession and consolidation of their businesses or companies.
The Small and Medium Enterprise Agency positioned the promotion of business revitalization through succession, reorganization, and consolidation as a priority measure for FY 2018 and later. The SME Unit will continue to use these loan programs to support SMEs that are undertaking business or company succession and consolidation.
Supporting the growth of businesses
- Businesses that have utilized JFC funds are flourishing in many fields
A total of 783 businesses (Note) have gone public after receiving support from the SME Unit, representing roughly 20% of all Japanese businesses that are publicly held. Many of these are flourishing as leading companies in Japan.
The number of businesses going public after receiving support from the SME Unit since 1989 is 618 (Note), accounting for roughly 20% of the total number of businesses that went.
Note: The number of publicly listed businesses is as of March 31, 2023 (excluding delisted businesses and businesses that have dissolved due to merger, etc.).

Credit Insurance Programs
Facilitating the smooth flow of funds to SMEs and micro/small businesses by working together with the Credit Guarantee System
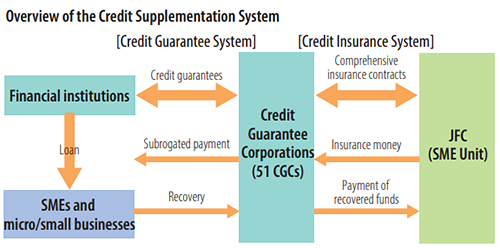
- Role of the Credit Insurance System
The SME Unit insures guaranteed liabilities (credit guarantees) provided by CGCs to SMEs and micro/small businesses that fall short in terms of collateral or creditworthiness when raising funds from financial institutions or issuing corporate bonds. Instituted under the Small and Medium-sized Enterprise Credit Insurance Act (Act No. 264 of 1950), the purpose of the Credit Insurance System is to promote the development of SMEs and micro/small businesses by insuring guarantees for SME loans and similar liabilities. It is designed so that the Credit Insurance System and the Credit Guarantee System together facilitate the smooth supply of business funds for SMEs and micro/small businesses. This mechanism is known as the Credit Supplementation System and plays a vital role in the Japanese government's SME finance policy.
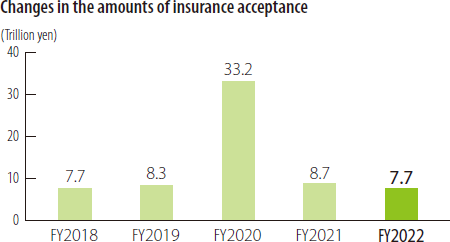
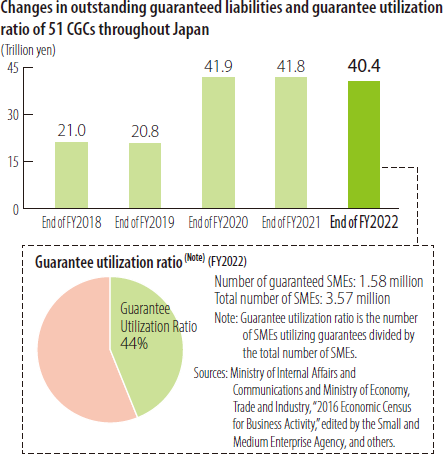
- 44% of SMEs Utilize the Credit Supplementation System
As of March 31, 2023, the portion of outstanding loans to SMEs guaranteed by CGCs (outstanding guaranteed liabilities) amounted to 40 trillion yen, accounting for 12% of all loans to SMEs.
Moreover, 1.58 million SMEs and micro/small businesses, accounting for 44% of all SMEs in Japan, were raising funds with the support of the Credit Guarantee System.
By providing insurance on such guarantees, the Credit Insurance System is contributing to the management stability of SMEs and micro/small businesses, and to their growth and prosperity by facilitating smooth flow of funds.
Securitization Support Programs
- Supporting the smooth supply of unsecured funds by private financial institutions using securitization methods
The securitization of loan claims for SMEs is conducted from the standpoint of ensuring smooth facilitation of SME financing.
In FY2022, the "synthetic CLO of regional financial institutions (Clover 2023 LLC)" was issued in the securitization support purchasing business. Besides entering into credit default swap (CDS) contracts with 39 regional financial institutions, the SME Unit acquired 10.9 billion yen of the 39.9 billion yen in corporate bonds issued by the special-purpose company (SPC) (Clover 2023 LLC), and also guaranteed 5.0 billion yen in the bonds. 41.0 billion yen in unsecured loans were provided to 1,943 businesses in 38 prefectures by this CLO.
By appropriately sharing the credit risks, credit analysis and administrative burdens of securitization, the SME Unit offers securitization methods convenient for private financial institutions to smoothly supply unsecured funds to SMEs and to diversify the means by which SMEs can obtain funds. While fulfilling its pioneering roles as a policy-based financial institution, the Unit will also contribute to the promotion and development of the securitization market.
Methods of securitization support
| Purchase-type | Guarantee-type |
|---|---|
| Operations that involve the securitization of unsecured SME loan claims, etc., acquired by way of transfer from private financial institutions or the use of credit default swap (CDS) contracts | Operations that involve the partial guarantee of unsecured SME loan claims, etc., securitized by private financial institutions as well as the guarantee of partial purchase of securitized instruments |